Media | Race | Demographics
MPR News Source Diversity Report, February 2021 - April 2022
DOCUMENTATION
REPORT: Detailed results of MPR News’ source diversity data analysis
EDITOR’S NOTE: Sarah Glover, Managing Editor of MPR News, responds to source diversity report
RELATED
MINNESOTA’S DIVERSE COMMUNITIES SURVEY: News Consumption and Trust in the Media
APM RESEARCH LAB SURVEY: Changing Racial Narratives in Media
NPR: New On-Air Source Diversity Data For NPR Show Much Work Ahead
by APM Research Lab | July 14, 2022
In February 2021, MPR News implemented a procedure to systematically track the following data on sources interviewed or otherwise featured in digital and broadcast stories or news shows: race/ethnicity, age, pronouns, place of residence and source role.
The APM Research Lab, at the invitation of MPR News leaders, examined the source data collected from February 2021 through April 2022 to provide the newsroom with a year-in-review report of trends and insights into source diversity. The goal of this report is to provide an understanding of who appears in the newsroom’s content and to establish benchmarks against which future newsroom goals can be measured.
The findings from our analysis were presented to MPR News editors, journalists and staff on July 1. MPR News Managing Editor, Sarah Glover, responded to the findings and articulated next steps for the newsroom in an Editor’s Note. Our key findings from the data are summarized below with additional detail available in a longer report on the subject.
Key Findings
APM Research Lab examined the source diversity data in aggregate and compared it, where relevant, to the demographics of Minnesota’s population. The following high-level trends and significant data points emerged from our analysis:
Race
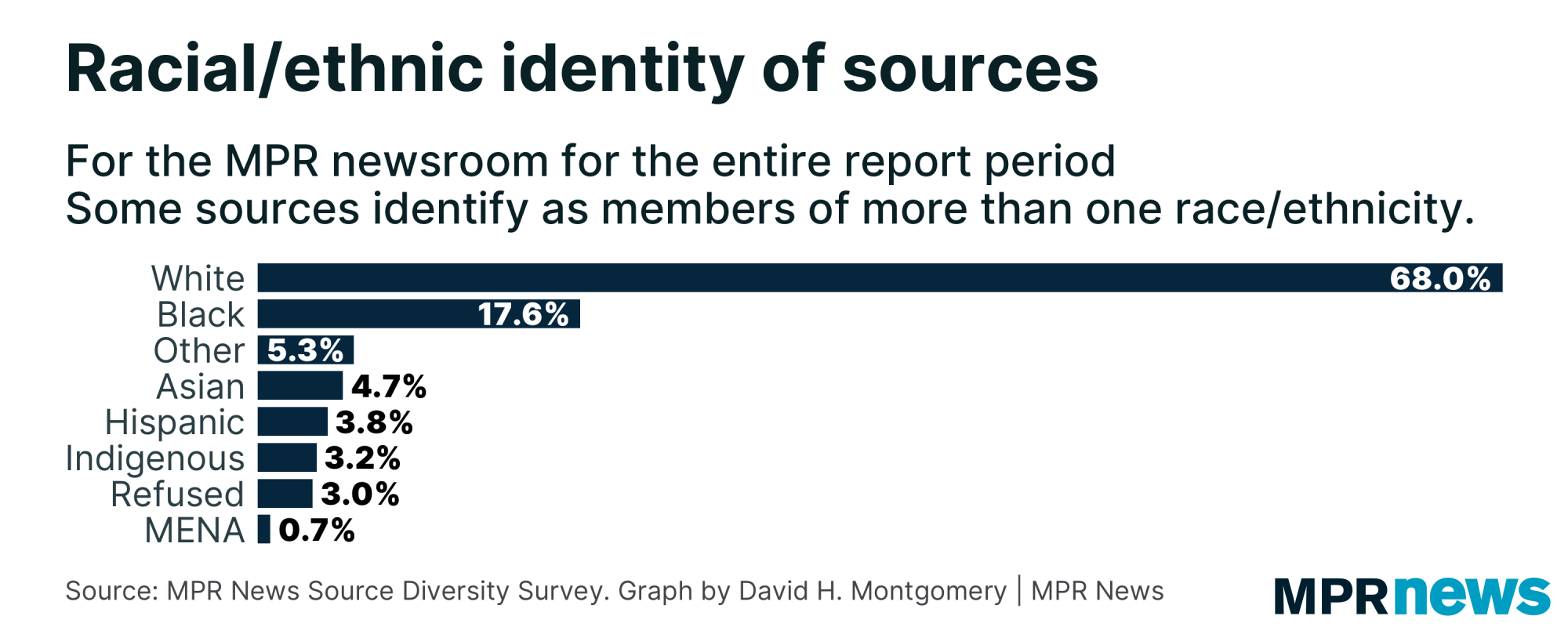
Black, Indigenous and people of color (BIPOC) sources represent 30% of sources MPR News interviewed, while around 24% of the population identifies as BIPOC in Minnesota overall. 3% of sources declined to answer.
67% of all sources identified as non-Hispanic white alone, which is less than the 76% of Minnesotans who identify as non-Hispanic white alone in the state overall.
Asian, Hispanic, Middle Eastern or North African (MENA) and Indigenous sources skew toward using she/her pronouns—Asian sources, in particular, lean heavily toward individuals using she/her pronouns. White and Black sources skew toward using he/him pronouns.
Place of Residence
As compared to the distribution of the state’s population, sources living in the central cities are overrepresented, while those in the suburbs and greater Minnesota are underrepresented. Of the sources who provided their residence and are from Minnesota, 47% were from Minneapolis or St. Paul, 23% were from the suburbs of the Twin Cities and 30% were from Greater Minnesota. This is compared to a state population distribution of 13% residing in Minneapolis and St. Paul, 42% in the Twin Cities suburbs and 45% in Greater Minnesota.
The proportion of BIPOC (Black, Indigenous and people of color) sources within each residential grouping (Minneapolis/St. Paul, Metro suburbs, Greater Minnesota) are fairly similar to the respective population share of BIPOC residents in each area. of the sources who reside in the Twin Cities suburbs, 27% identify as BIPOC, which is the same share of BIPOC Minnesotans within the overall population residing in the metro suburbs. Slightly fewer sources from Minneapolis or St. Paul identified as BIPOC (41%) compared to the share of the Twin Cities’ population that identifies as BIPOC (46%), while slightly more sources from Greater Minnesota identified as BIPOC (17%) compared to their share of the region’s population (14%).
Age
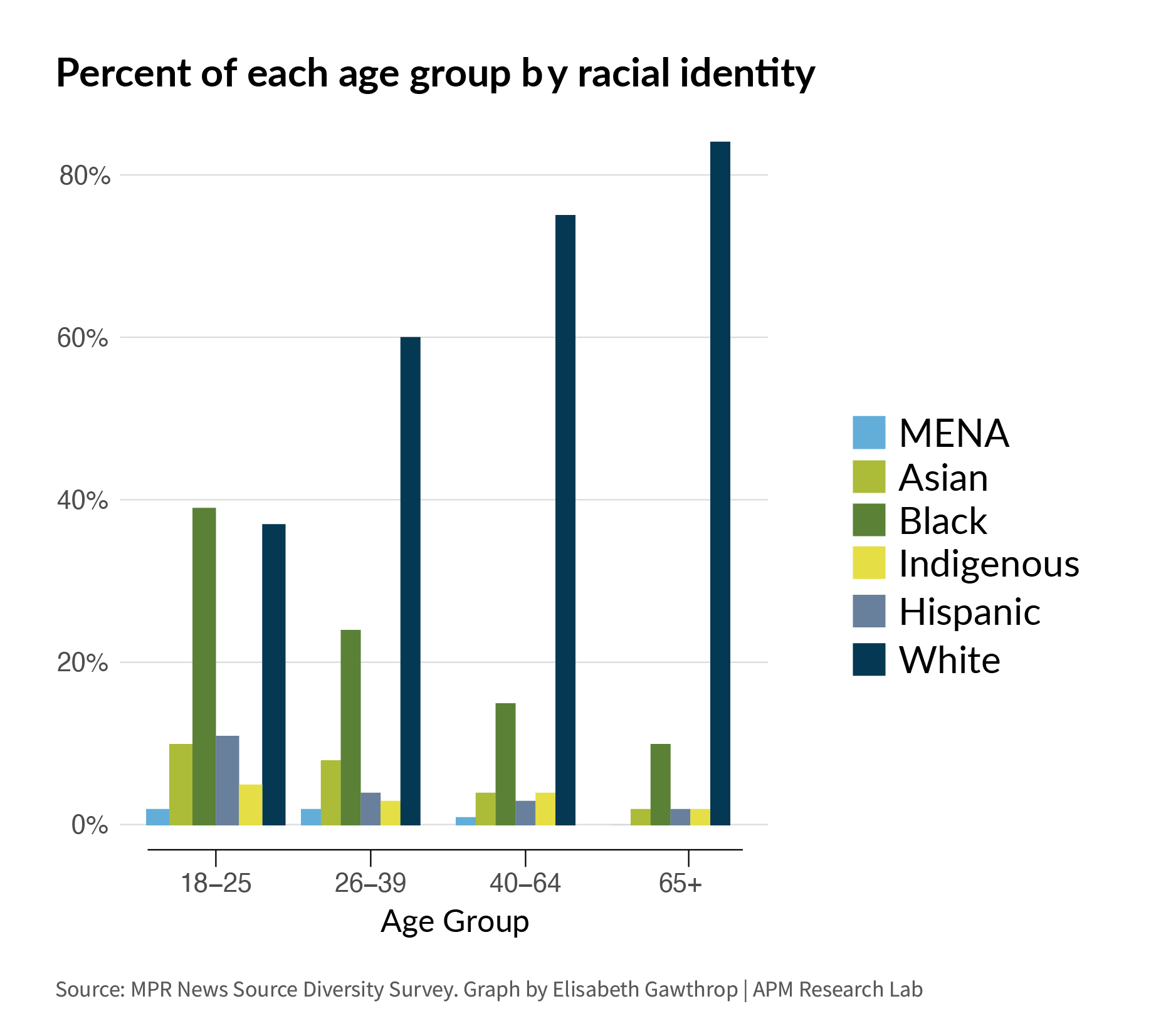
54% of MPR News sources are in the 40-64 age range, but only 31% of Minnesotans fall into this age group. Most of the sources in this range are experts or officials.
Sources between the ages of 18 and 25 are more racially diverse than other age groups, and source diversity decreases as source age increases. This young-adult age group is the only one in which a plurality of sources are Black (39%). In all other age groups, the majority of sources are white.
Role of Source
68% of sources MPR News interviewed were either experts (35%) or officials (33%).
The roles of spokesperson, officials and expert skew heavily white and toward individuals using he/him pronouns. Spokesperson and official sources are most likely determined by forces external to the MPR Newsroom. However, there is greater potential for seeking diverse voices among expert sources.
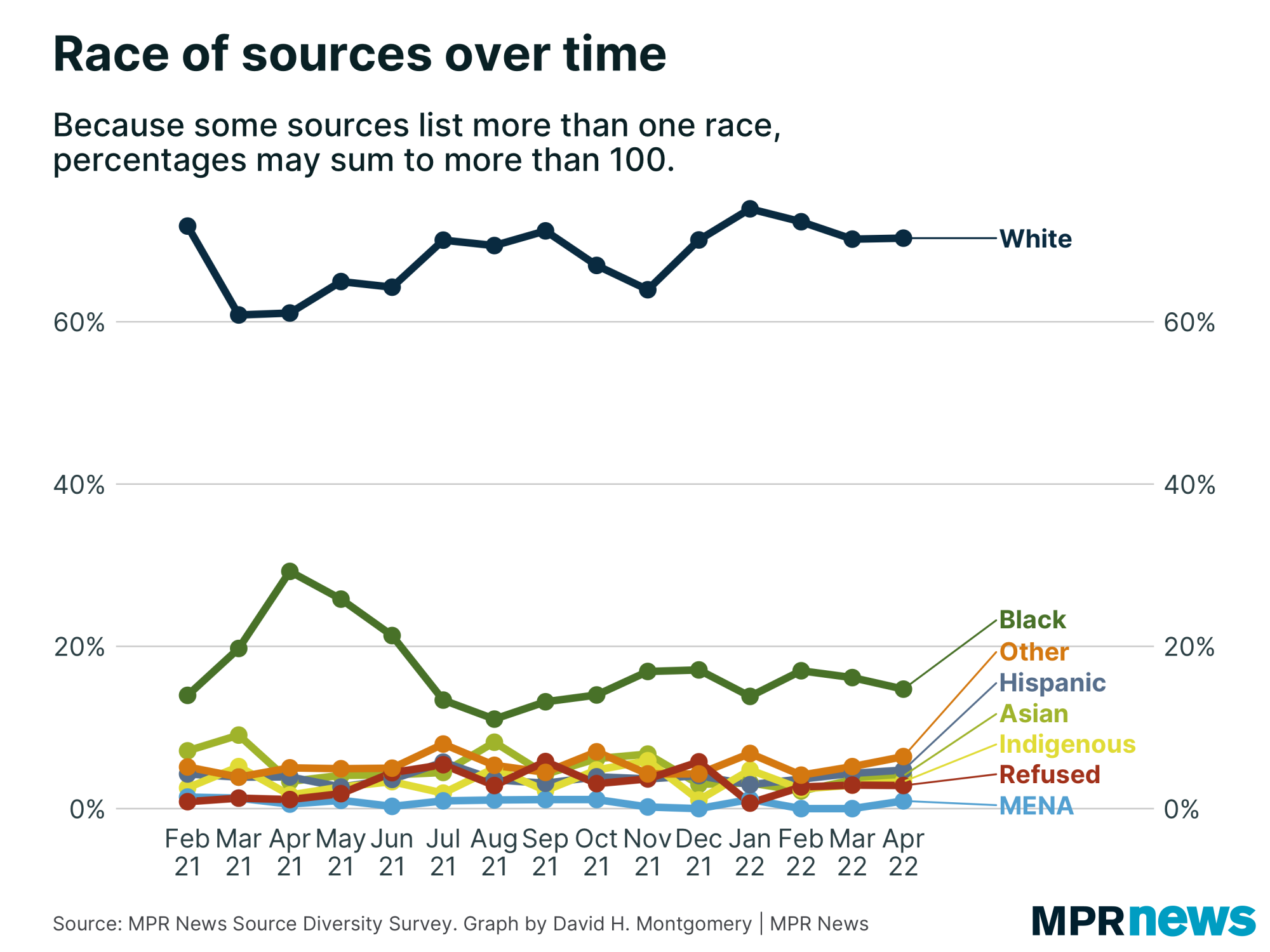
Trends over Time
Overall, the racial makeup of sources did not change significantly over the period covered in this report. A notable exception is that more Black Minnesotans were interviewed as sources—particularly as activists and vox pop (meaning “voice of the people,” including general public or “person on the street”-type sources)—in the spring of 2021, which coincided with Derek Chauvin’s trial and the related one-year anniversary of George Floyd’s murder.
Analysis of sources by role
In addition to high-level trends, the APM Research Lab also organized our findings by specific roles. Reporters and producers were instructed to consider the role of the source in the story in which they were being featured, not necessarily what the source’s job title or other identity might be, unless they were bringing that expertise to the story.
As mentioned above, the role of “expert” was the most common type of role occupied by sources in the stories or broadcasts for which they were interviewed. Over one-third, 35%, of all sources interviewed from February 2021 through April 2022 were experts. “Official” was the second most common role of sources, with 33% of all sources in that role, and 17% of sources were interviewed as vox pop. Twelve percent of sources were interviewed as activists, 6% were artists, 5% were interviewed in another capacity, and just 2% were spokespersons.
The roles of spokesperson, official and expert skew heavily white and toward individuals using he/him pronouns.
Spokespersons and officials each have a large majority of white sources, 88% and 79% respectively, but this likely reflects the dynamics of these sources’ institutions. Officials also have the largest disparity between sources using he/him pronouns and she/her pronouns.
About three-quarters of expert sources are white (72%), and there is a sizeable disparity between white expert sources using he/him pronouns (37%) and white experts using she/her pronouns (29%).
Officials or experts were the majority role for sources in every racial group.
The roles of activist, artist and vox pop sources skew toward people using she/her pronouns.
·Compared to their share of the Minnesota population (76%), white sources are underrepresented in their role as vox pop sources (59%). Black sources are overrepresented as vox pop sources, as compared to their population share (25% to 7%).
However, the proportions of Hispanic, Asian and Indigenous sources in the vox pop role are comparable to their share of Minnesota’s population. (Hispanic: 7% of vox pop sources, 6% of Minnesota’s population; Asian 5% of vox pop sources, 5% of the state’s population; Indigenous 3% of vox pop sources, 1% of the state’s population.)
See our detailed report for a full analysis of sources by role.
For media inquiries, contact: Ellie Pierce, epierce@americanpublicmedia.org, 651-290-1233.